Analysis of eSports as a commercial activity


Published: March 5, 2018
Latest article update: Dec. 12, 2022
Abstract
T he article deals with eSports as a perspective kind of commercial activity. The research urgency is determined by the fact that, given the active increase of eSports market with growth rates of more than 30% per year, the types of commercial activities in this field and in scientific papers are not studied in an adequate degree. T he purpose of the article is to evaluate the commercial activity development in eSports and to determine the perspectives for its further growth in Ukraine. In order to determine the key types of commercial activity in eSports, the main sources of revenue in this area compared to sports were investigated, which showed a large unrealized potential for increasing revenues from the sale of tickets to competitions, the realization of broadcasting rights and merchandising. The study also showed that the largest number of income sources in eSports is at the stage of cyber-tournaments, which can be explained by a large consumer audience at this stage. However, unlike the world practice, computer game producers and well-known manufacturers of consumer goods in Ukraine do not finance domestic competitions, and, therefore, this stage of commercial activity remains at a low level. In modern conditions, among the types of eSports activities in Ukraine, only the computer games production and the cyber-racers game are properly developed. According to authors, to improve the eSports development in Ukraine, creating the national system of regular eSports competitions is needed, which will form the basis for the development of most types of commercial activities that are part of the cybertournaments. To do this, one needs to create appropriate platforms, as well as improve communications with fans in social networks and at amateur competitions. All this will make eSports a highly profitable business in Ukraine
Keywords
Income, sports economics, sports organization, Ukraine, cyber-tournaments, commercial activities, eSports
INTRODUCTION
Computer sports (cybersports, eSports) is defined as a video games competition that takes place in a virtual space. Experts from the SuperData analytical agency show that in 2015, the total turnover of the eSports industry was USD 747 million, and in 2018 it is expected to reach USD 1.9 billion (SuperData Report, 2016). These are extremely high rates. That is, computer games that were once innocent fun in the modern economy are becoming the leader of the commercial sector of sports services.
However, according to 2016 statistics, in Ukraine, the share of services of art, sports, entertainment and recreation provided to the population was only 1.7% in the total amount of consumer services (Statistics of Ukraine, 2016). It is difficult to separate the share of sports services in Ukraine, because such information is not available in statistics. But, of course, this figure does not exceed 1%. In Russia, the development of sports services is also negligible: according to 2016 data, sport services accounted for only 0.8% of revenues from paid services to the
population (Statistics of Russian, 2017). And in developed European countries and in the USA, the share of sports in the total revenues of the service sector is more than ten times.
Consequently, the potential for further development of sports income and profits, in particular from cybersport, is significant in Ukraine. Identifying promising types of eSports activities that have a significant potential for growth and capable of providing substantial profits can create the necessary data base for entrepreneurs to further develop their business in this area.
The Newzoo research results have shown that the impetus for a sharp increase in incomes and profits from eSports in the world has become a model of commercial approach to the activities of this market participants (Newzoo, 2016).
Thus, the practical benefit of studying eSports as a kind of commercial activity is also practically assured, and its theoretical justification requires the corresponding work, that is, reflects the relevance of the subject chosen.
The purpose of the research is to evaluate the commercial activity development in eSports and to determine its most promising species for further distribution in Ukraine.
1. LITERATURE REVIEW
Modern scholars and practitioners pay great attention to determining the eSports belonging to a particular industry. In the academic literature, active debates exist as to the place of eSports: is it a type of entertainment, or rest, or sports?
In support of eSports being an entertainment industry, scientists argue that large-scale championships are taking place in computer games, which simultaneously attract a large number of people as spectators. PricewaterhouseCoopers has conducted a study on eSports as part of the entertainment industry and published the report (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2017).
Seo considers eSports as an element of the recreation field, he believes that eSports tourism is actively developing in modern society, and the market for these services is actively increasing (Seo, 2016).
But the idea that eSports is a sport is the most common. Thus, Hallmann and Giel note that eSports has five main features of sport (Hallmann & Giel, 2017). Heere argues that cyber sports should be considered as part of sport management (Heere, 2017). Funk, Pizzo and Baker are of the same opinion (Funk, Pizzo, Baker, 2017).
In recent years there have been the first works in which interest in eSports is in its study from the standpoint of entrepreneurial, commercial activity, which is defined as activity for profit (Tsybuliov, 2011). Among such researchers Voskolovych and Khaidarov (2016) can be identified, who found that eSports revenues are the main source of in come in this sector (Voskolovych & Khaidarov, 2016). The authors offer a very detailed classification of income from this sport.
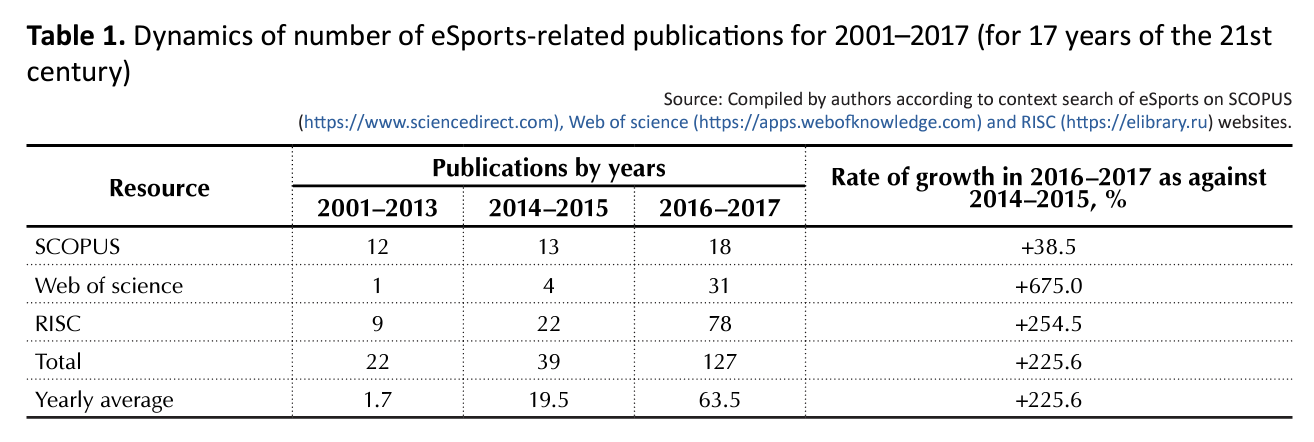
The study of modern scholars’ publications, which are contained in SCOPUS, Web of science and RISC, showed that in general, the number of researches on eSports is quite small (Table 1).
As we see, over the past two years, the number of eSports publications has increased more than three times as to the previous two years. But while studying the content of the available literature, one can conclude the researches on economic issues are artificial.
In addition, there is no quotation for the economic researches contained in the resources shown in Table 1. This shows the weakness of the systemic scientific and economic knowledge on eSports.
That is, the practice of commercial activity in eSports is currently far ahead of the scientific substantiation of this type of activity
2. KEY RESEARCH FINDINGS
Today, any sport has become a commercial activity, and in some of its forms it is a big business. The development of sport through commercial enterprises and the commerce development with the help of sport are two counterprocesses with high prospects for all participants’ profitability (B2Blogger.com, 2008).
eSports and the commercial sector symbiosis is a complex, multidimensional process, but considering the ultimate goal of commerce, we propose to analyze it in the context of identifying profit sources, which will enable real and potential actors to decide on the prospects of participation and development of this area.
To understand the main sources of income in eSports, a study of volume and structure of revenues in the industry was conducted (Table 2).
It must be said that different analytical agencies give different forecasts of expected revenue volumes. For example, PricewaterhouseCoopers estimates it at USD 327 mln in 2016 (PWC, 2017). That is, the figure is less than tree times, compared to the data in the table. But we believe that such a rotation in the estimates is related to the differences in the industries, to which eSports is related. That is, if we consider eSports as part of the entertainment industry, as PricewaterhouseCoopers does, then the proceeds will be smaller due to lack of revenue from sponsors and other sources that are not taken into account in this area.
As can be seen from the table, eSports revenues are more than 160 times less than the sports industry revenue. But if we take into account that there are about 60 summer and winter disciplines in the Olympic sport (their list and number are unstable), and in general there are more than 200,000 kinds of sports, then the long-term benefits of commerce in eSports are also practically assured.
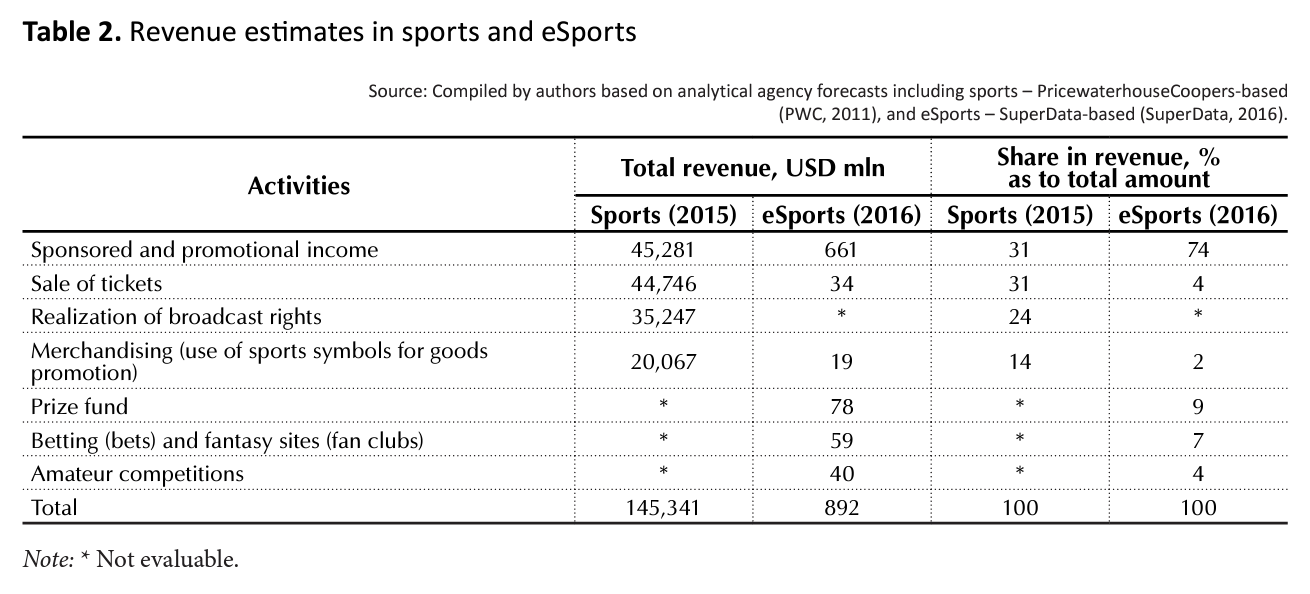
If we compare the structure of income sources in sports and in eSports according to Table 2, then it is possible to note the large unrealized potential for further growth in revenues in eSports from the sale of tickets to competitions, the realization of broadcasting rights and merchandising. The most efficient businessmen have already realized such opportunities to earn significant profits and now they are building stadiums for cyber sports.
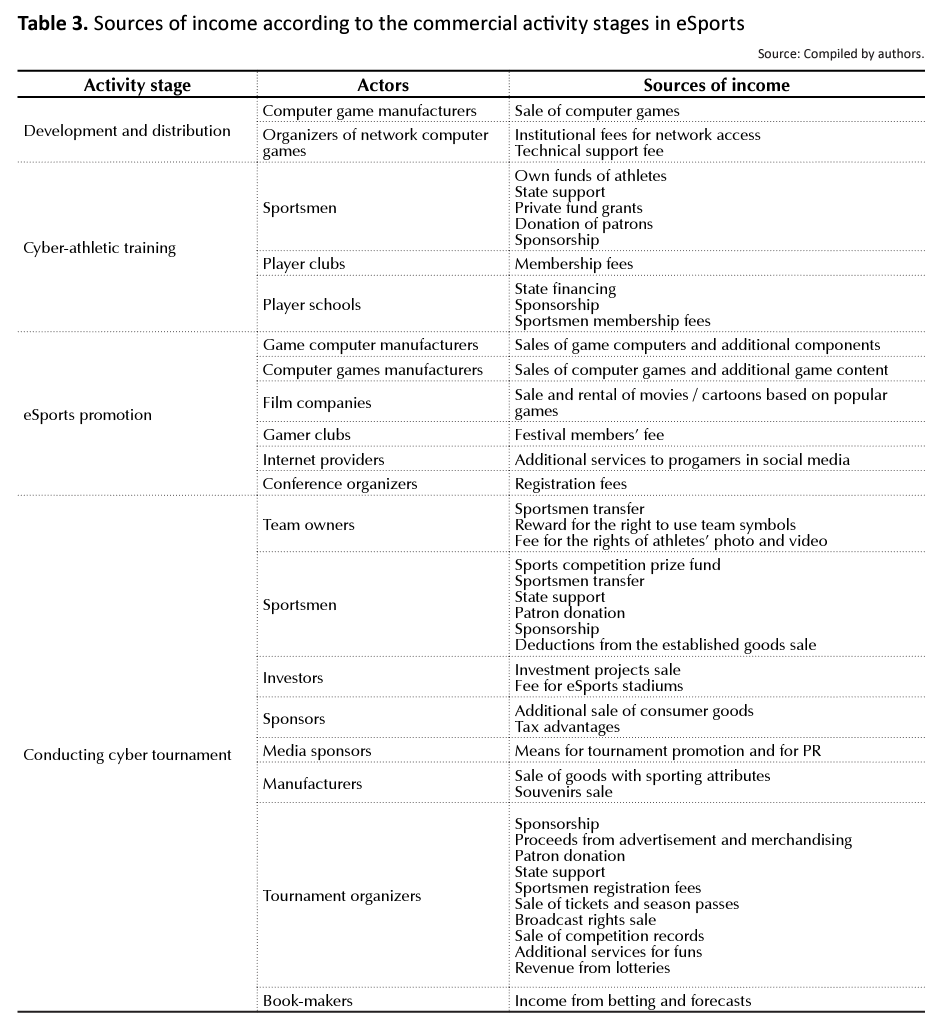
It should be noted that in the table, sources of income in eSports are limited to six types, while in practice their spectrum is much larger. Therefore, the authors systematize sources of income in eSports in detail (Table 3).
As can be seen from Table 3, the largest range of income sources in the eSports industry is at the tournament stage.
It should be noted that nowadays, the main profits from eSports are obtained by computer game manufacturers and game computer manufacturers, because they fund world-class championships where they act as sponsors. Such championships are a platform for their main products advertisement (Ukrainian Reality, website, 2016).
But in recent years, traditional business representatives are also actively integrating into the electronic sports market as tournament sponsors. Large amounts of eSports financing are provided by consumer goods manufacturers with well- known brands, including Coca-Cola, Red Bull, Visa, Audi, and Gillette (eSport Conference, 2017).
According to Newzoo reports, revenues from advertising are the key component of the eSports economy. According to Newzoo, total advertising revenue was 71% of all industry revenues in 2016. The rest is the proceeds from the sale of tickets and related products at competitions (Newzoo, 2016).
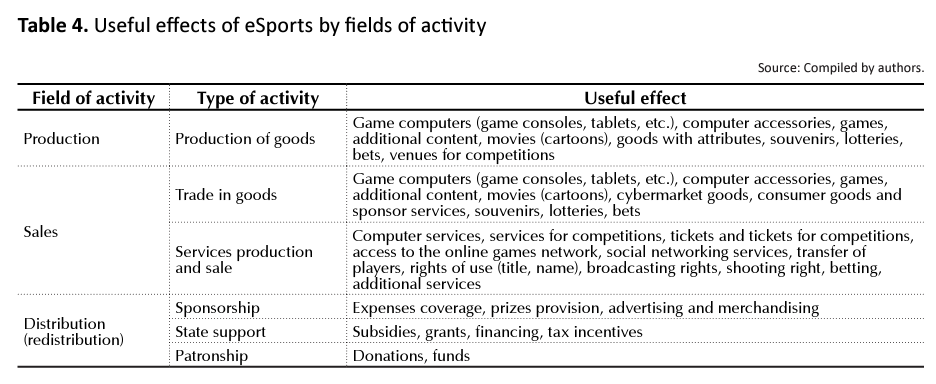
Table 4 determines the types of eSports advantages that may be the subject of commercial activity.
The table shows that in the turnover field, there is the largest range of commercial products that can be offered on the market for a commercial effect.
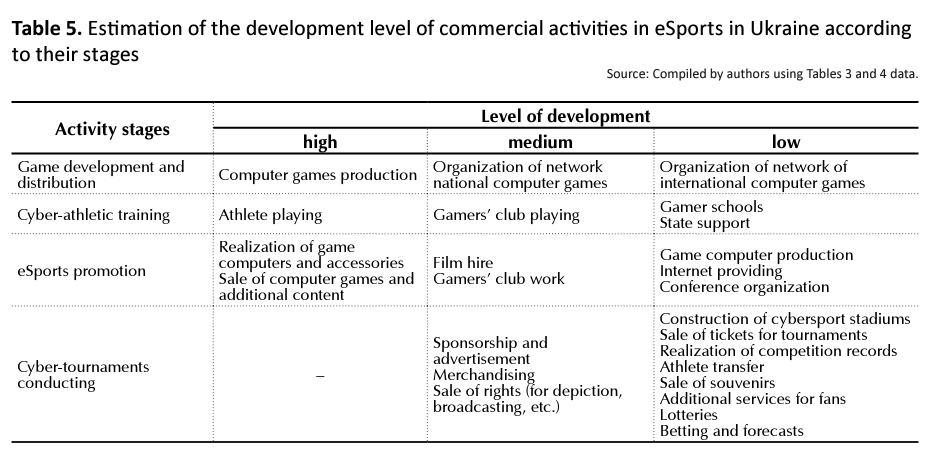
Based on the data presented in Tables 3 and 4, the development of certain types of eSports activities in Ukraine can be estimated. To do this, Table 5 identifies activities that are high, medium, and low for this industry.
As you can see, although the activities of the cyber-tournaments are the most profitable, as was found in Table 3, but its development in Ukraine is low and needs to be intensified (Table 5).
Current research shows that eSports industry is promising for Ukraine, as evidenced by the First Conference in Ukraine dedicated to investment and integration of Ukrainian business in the eSports market (eSport Conference, 2017). We accede to the submission because:
- the annual global growth of the market is more than 30%;
- in recent years Ukraine ranks 5-6 in the world among the countries with the most developed eSports branch;
- it is projected that in 10 years, eSports will become even more popular than football;
- among the participants of the most famous eSport-tournament The International in 2015, there were 12 players from Ukraine and only representatives of China exceeded the number.
Given the research results, we determine the following directions for further eSports development in Ukraine:
- comprehensive online user promotion;
- support for talented cyber-racers and successful cyber-teams;
- organization of cyber schools and eSports clubs;
- increasing the number of domestic eSports tournaments, including international ones;
- creation of domestic computer technology and expansion of the original games development;
- construction of cybersport stadiums;
- promotion of sponsorship, advertising and merchandising in eSports activities;
- bookmaking development.
It should be noted that eSports development in Ukraine, as well as the development of any commercial sphere, involves a social component, i.e.: job creation, tax deduction, etc. Besides this, eSports development makes it possible to ensure communication between cyber-sportsmen from different countries, the formation of computer literacy and eSports culture.
Unfortunately, eSports in Ukraine is not funded at the state level, although in 2010 the eSports Federation of Ukraine was created. A number of countries, including China, South Korea, Malaysia, the Philippines, France and Russia, have recognized eSports as an official sport. In the UK and Sweden, the government is working to recognize eSports as a sport. And in the United States, one computer game (League of Legends) is officially fitted to sports (Shirobakina, 2016).
According to the authors, state regulation bodies of the Ukrainian economy should pay due attention to domestic eSports and give it the necessary support, because this branch has all the features to become in the future one of the most important for the country’s business and economy.
CONCLUSION
The research allowed to make the following conclusions.
- eSports commercial activity in Ukraine is gradually developing. In this area, there are a number of actors who already receive high incomes and direct their actions to the commercial effect growth. Computer games production and cyber-racers game demonstrate high level development.
- Other types of eSports activities in Ukraine are far behind, which can be explained by the lack of active work on the organization and conduct of the cyber-tournaments, first of all - at the international level. That is, in order for domestic eSports to develop actively, it is necessary to establish a national system of regular cyber-tournaments at special platforms.
- For further eSports development in Ukraine it is necessary to expand the types of activities in this area. First and foremost, attention should be paid to the development of the audience and communication with fans, which should be developed by groups in social networks, fan clubs, amateur competitions, etc. This will increase the level of manageability, expand the contingent of fans, and will create conditions for further development of other, most profitable types of eSports activities, namely: sponsorship, advertising, and merchandising.
REFERENCES
- 2016 eSports Market Report.
- Heere, B. (2017). Embracing the sportification of society: Defining e-sports through a polymorphic view on sport. Sport Management Review, 18.
- Daniel C. Funk, Anthony D. Pizzo, Bradley J. Baker (2017). eSport management: Embracing eSport education and research opportunities. Sport Management Review, 23.
- eSports revenues for 2016 adjusted upward to $493m.
- Kirstin Hallmann, Thomas Giel (2017). Esports – competitive sports or recreational activity? Sport management review, 31.
- Report: The eSports market is worth $747M.
- Shirobakina, E. A. (2016). Cyber sport: from just a hobby to a professional sport. Fizicheskoye vospitaniye i sportivnaya trenirovka, 3(17), 60-63.
- Tsybuliov, P. M. (2011). Комерціалізація інтелектуальної власності наукових організацій шляхом створення spin-off компаній [Komertsializatsiia intelektualnoi vlasnosti naukovykh orhanizatsii shliakhom stvorennia spin-off kompanii].
- Voskolovych, N. A., & Khaidarov, K. A. (2016). Организация и финансирование соревнований в киберспорте [Organizatsyia i finansirovanie sorevnovaniy v kibersporte]. Azimut nauchnykh issledovaniy: ekonomika i upravleniye, 3(16), 79-82.
- Yuri Seo (2016). Professionalized consumption and identity transformations in the field of eSports. Journal of Business Research, 69(1), 264-272.
- Всемирный обзор индустрии развлечений и СМИ: прогноз на 2017–2021 годы [Vsemirnyy obzor industrii razvlecheniy i SMI: prognoz na 2017–2021 gody].
- Dota 2 Esports Betting Analysis. Perspectives for 2018
- Діяльність підприємств сфери послуг у IV кварталі 2016 року. Статистичний бюлетень [Diialnist pidpryemstv sfery posluh u 4 kvartali 2016 roku. Statystychnyi biuleten].
- Supreme Court: esports betting can get out of the shadows
- Коммерциализация спорта: смерть идеалов или перспектива развития [Kommertsializatsiya sporta: smert idealov ili perspektiva razvitiya].
- Нужна ли Украине национальная сборная по киберспорту [Nuzhna li Ukraine natsionalnaya sbornaya po kibersportu].
- Первая конференция в Украине, посвященная инвестициям и интеграции украинского бизнеса в рынок киберспорта eSPORTconfUkraine 22 февраля 2017 [Pervaya konferentsiya v Ukrayne, posviashchennaya investitsiyam i integratsii ukrainskogo biznesa v rynok kibersporta. eSPORTconfUkraine 22 fevralia 2017].
- Supreme Court Open the Esports Betting Door
- Перспективы развития мировой индустрии спорта до 2015 года [Perspektivy razvitiya mirovoy industriyi sporta do 2015 goda].
- Россия в цифрах 2017: Крат. стат. сб. [Rossiya v tsifrakh 2017: Krat. stat. sbornik (2017)].
- Senate Bill 240 will modify the Nevada statutes regarding pari-mutuel betting systems





